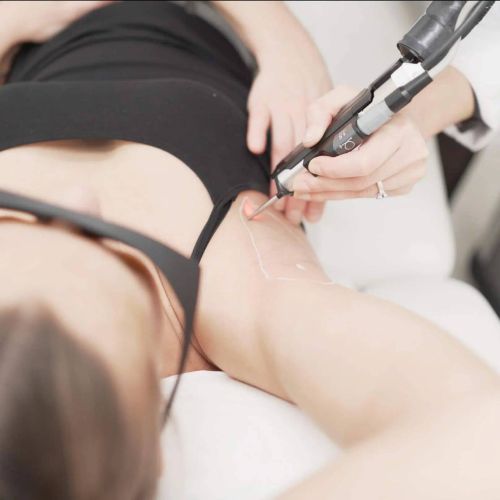
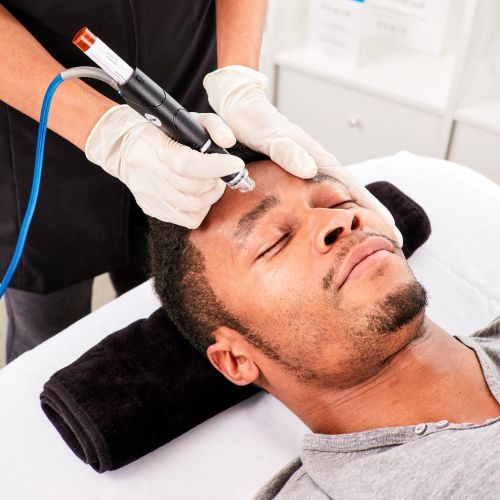
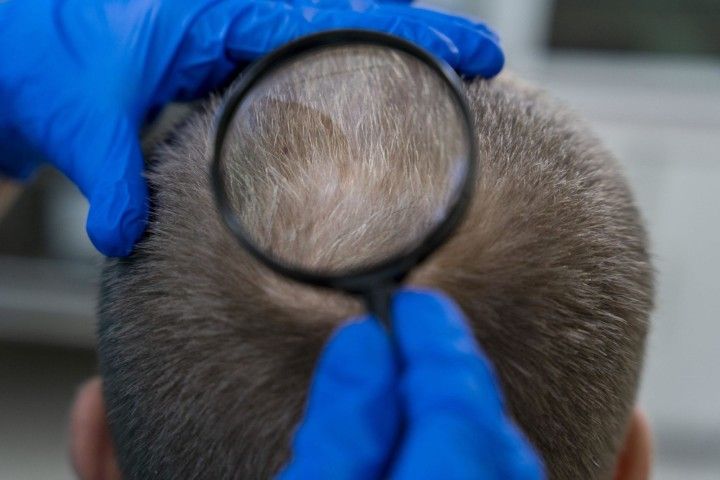
Vos prestations préférées
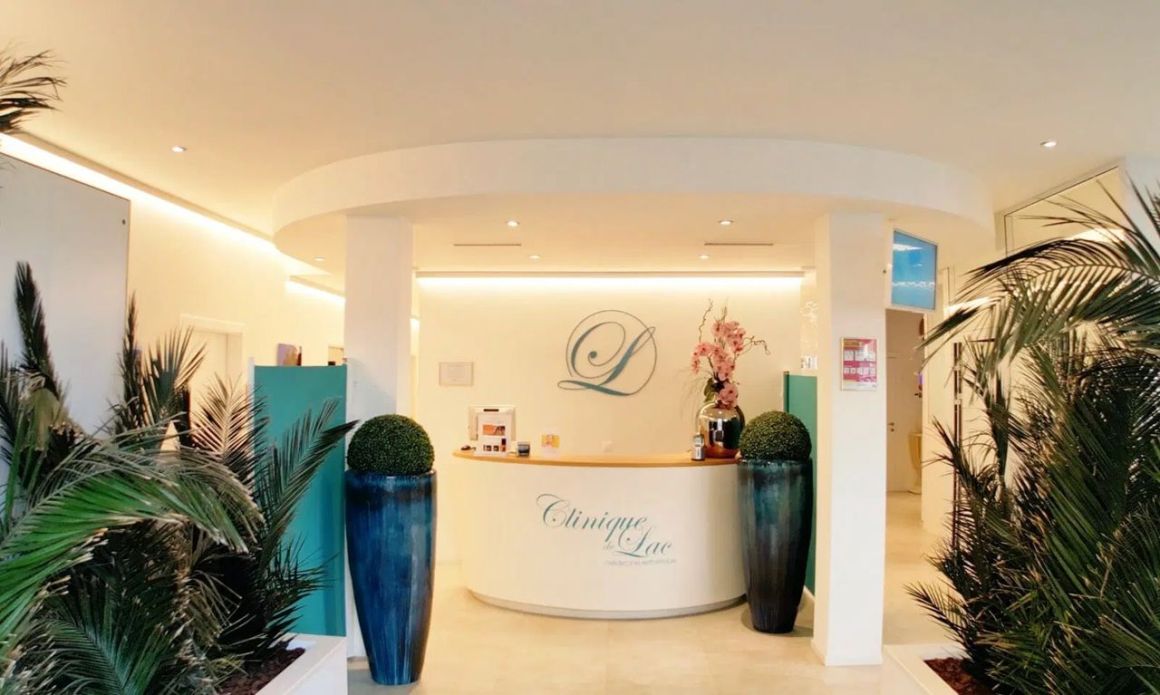
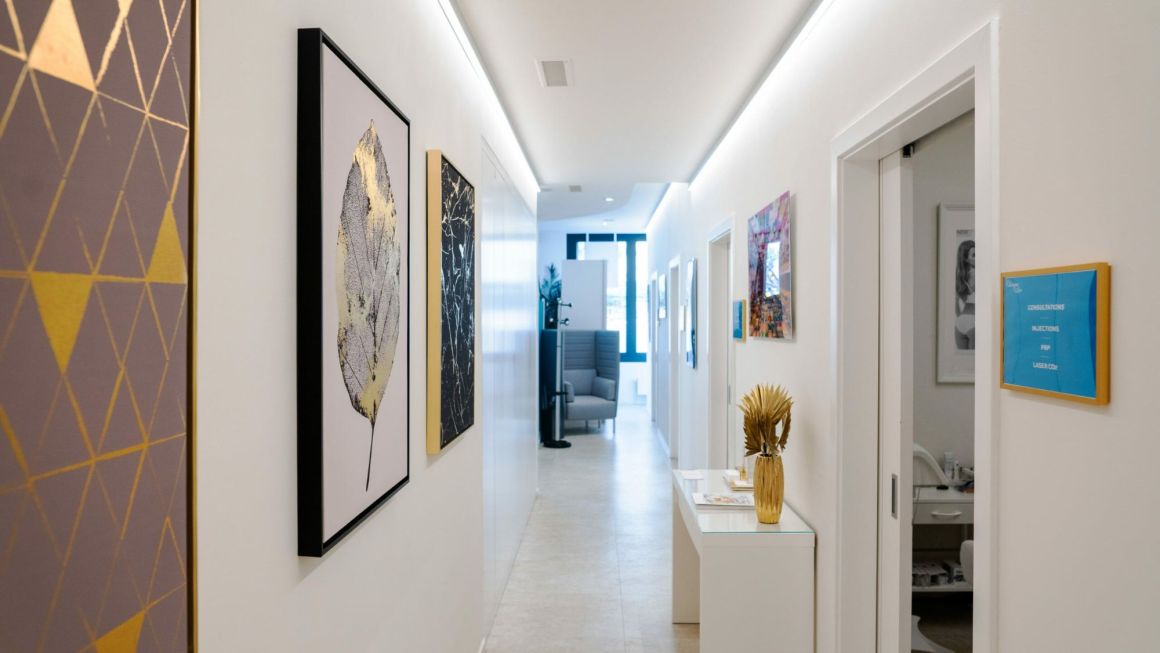
La Clinique du Lac, à la pointe de l’esthétique
Découvrez des soins innovants pour sublimer votre beauté avec expertise et raffinement.
Découvrir notre équipe Voir nos valeurs et nos normesLa clinique en quelques chiffres
Chirurgies réparatrices
Patients sur les 10 dernières années
%
De patients satisfaits
Spécialistes de santé à votre service






Nos technologies pour répondre à vos besoins
Découvrez nos solutions de traitements
Notre accompagnement
-
 La prise de votre rendez-vousDès votre premier contact, notre équipe vous guide dans la planification de votre rendez-vous. Nous prenons le temps d'écouter vos attentes, de répondre à vos questions et de vous orienter vers les solutions adaptées à vos besoins.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
La prise de votre rendez-vousDès votre premier contact, notre équipe vous guide dans la planification de votre rendez-vous. Nous prenons le temps d'écouter vos attentes, de répondre à vos questions et de vous orienter vers les solutions adaptées à vos besoins.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
-
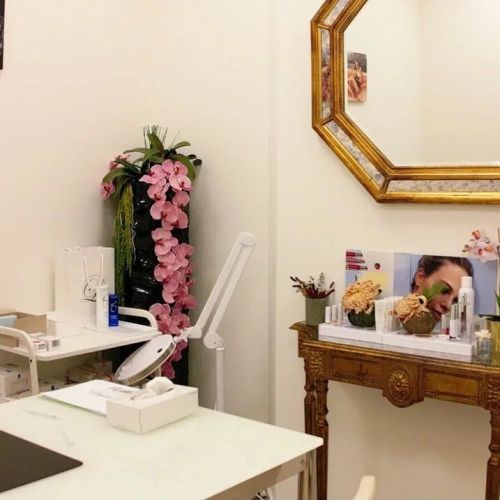 La mise en place de votre traitementLors de votre consultation, nos spécialistes élaborent un plan de traitement personnalisé. Nous vous expliquons chaque étape avec clarté et transparence pour garantir votre confiance et votre sérénité tout au long du processus.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
La mise en place de votre traitementLors de votre consultation, nos spécialistes élaborent un plan de traitement personnalisé. Nous vous expliquons chaque étape avec clarté et transparence pour garantir votre confiance et votre sérénité tout au long du processus.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
-
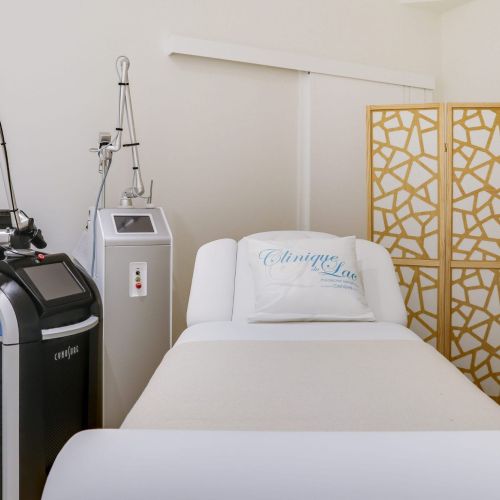 Le jour de l’interventionLe jour J, vous êtes accueilli(e) dans un environnement moderne et sécurisé. Nos équipes médicales veillent à ce que tout se déroule dans les meilleures conditions, avec professionnalisme et bienveillance.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
Le jour de l’interventionLe jour J, vous êtes accueilli(e) dans un environnement moderne et sécurisé. Nos équipes médicales veillent à ce que tout se déroule dans les meilleures conditions, avec professionnalisme et bienveillance.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
-
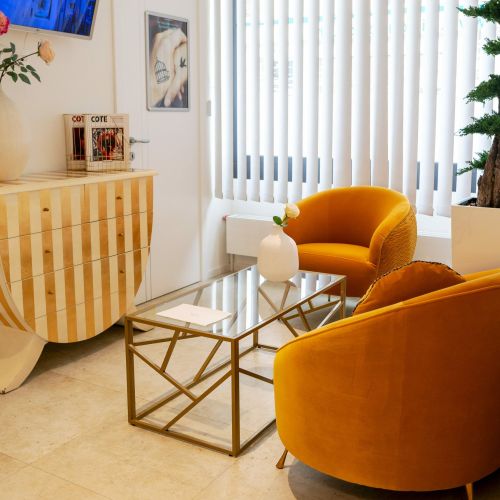 Après l’interventionNotre accompagnement ne s’arrête pas à l’intervention. Nous assurons un suivi post-opératoire rigoureux pour surveiller votre rétablissement et répondre à vos éventuelles questions, afin de garantir des résultats optimaux et votre satisfaction.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous
Après l’interventionNotre accompagnement ne s’arrête pas à l’intervention. Nous assurons un suivi post-opératoire rigoureux pour surveiller votre rétablissement et répondre à vos éventuelles questions, afin de garantir des résultats optimaux et votre satisfaction.Je souhaite prendre rendez-vous